The following table lists the safety functions integrated in ACOPOSmulti SafeMOTION inverter modules as well as the safety levels that can be achieved when they are used:
Safety function | EN ISO 13849-1 | EN 61508 / EN 62061 | Safe | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
EnDat 2.2 | SinCos | EnDat 2.2 | SinCos | ||
Safe Torque Off (STO) | PLe / CAT 4 | PLe / CAT 4 | SIL 3 | SIL 3 | No |
Safe Torque Off One Channel (STO1) | PLd / CAT 3 | PLd / CAT 3 | SIL 2 | SIL 2 | No |
Safe Operating Stop (SOS) | PLd / CAT 3 | Max. PLe / CAT 4* | SIL 2 | Max. SIL 3* | Yes |
Safe Stop 1 (SS1) | Time-based monitoring: | Time-based monitoring: | Time-based monitoring: | Time-based monitoring: | Time-based monitoring: |
Safe Stop 2 (SS2) | PLd / CAT 3 | Max. PLe / CAT 4* | SIL 2 | Max. SIL 3* | Yes |
Safely Limited Speed (SLS) | PLd / CAT 3 | Max. PLe / CAT 4* | SIL 2 | Max. SIL 3* | Yes |
Safe Maximum Speed (SMS) | PLd / CAT 3 | Max. PLe / CAT 4* | SIL 2 | Max. SIL 3* | Yes |
Safe Direction (SDI) | PLd / CAT 3 | Max. PLe / CAT 4* | SIL 2 | Max. SIL 3* | Yes |
Safely Limited Increment (SLI) | PLd / CAT 3 | Max. PLe / CAT 4* | SIL 2 | Max. SIL 3* | Yes |
Safely Limited Acceleration (SLA) | PLd / CAT 3 | Max. PLe / CAT 4* | SIL 2 | Max. SIL 3* | Yes |
Safe Brake Control (SBC) | PLd / CAT 3 | PLd / CAT 3 | SIL 2 | SIL 2 | No |
Safely Limited Position (SLP) | PLd / CAT 3 | Max. PLe / CAT 4* | SIL 2 | Max. SIL 3* | Yes |
Safe Maximum Position (SMP) | PLd / CAT 3 | Max. PLe / CAT 4* | SIL 2 | Max. SIL 3* | Yes |
Safe Homing | PLd / CAT 3 | Max. PLe / CAT 4* | SIL 2 | Max. SIL 3* | Yes |
Safe Brake Test (SBT) | - | Max. PLd / CAT 3* | - | Max. SIL 2* | Yes |
Remanent Safe Position (RSP) | PLd / CAT 3 | - | SIL 2 | - | Yes |
| * | Depends on the encoder used |
STO - Safe Torque Off
STO - Safe Torque Off
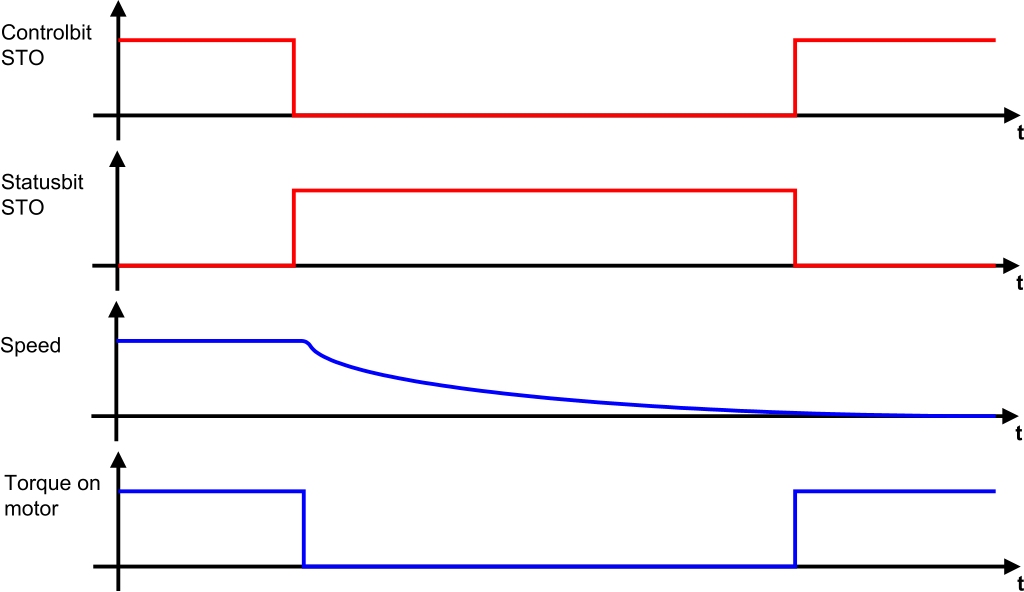
Safe Torque Off is the status in which the drive motor is no longer supplied with power (i.e. no torque and force being generated). The power supply to the drive is safely cut off by activating safe pulse disabling in a secure manner. Because the drive is no longer able to generate torque, it is impossible for any potentially dangerous movements to occur.
STO is made available to SafeLOGIC as an integrated safety function and can therefore be requested directly over the network, eliminating the need for external wiring.
The STO safety function provides the foundation for all other safety functions. As the implementation of the closed-circuit principle, it is applied every time an error occurs.
STO1 - Safe Torque Off 1
STO1 - Safe Torque Off 1

The STO1 safety function works in the same way as STO. The sole difference is that either only the HighSide or only the LowSide IGBTs are cut off depending on the configuration.
SOS - Safe Operating Stop
SOS - Safe Operating Stop
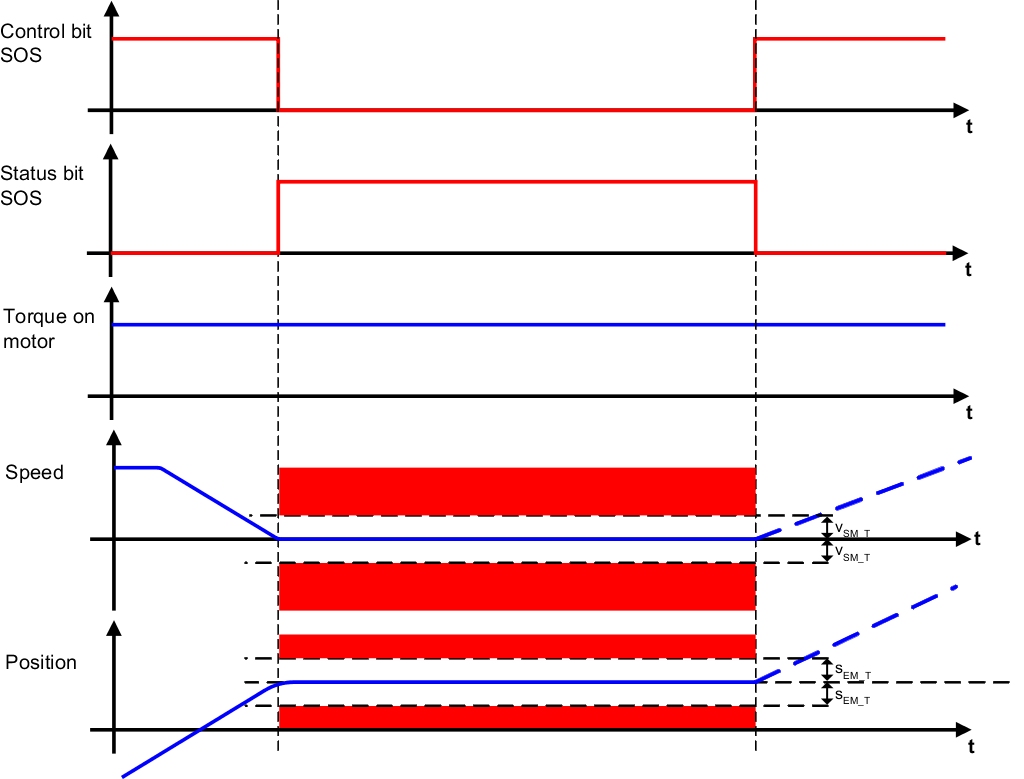
Safe Operating Stop (SOS) is the state in which the drive is monitored for coming to a safe stop. The drive is supplied with power and can therefore generate torque and force. All control functions between the electronic controller and the drive motor are active. The axis standstill is monitored using a configurable standstill tolerance window. Both the position as well as the speed are monitored. In order to collect the speed and position data in a safe manner, a suitable safety encoder is required. If the standstill monitoring limits are violated, safe pulse disabling is activated immediately and the drive switches to an error state that must be acknowledged.
Safe stop 1 (SS1)
Safe stop 1 (SS1)
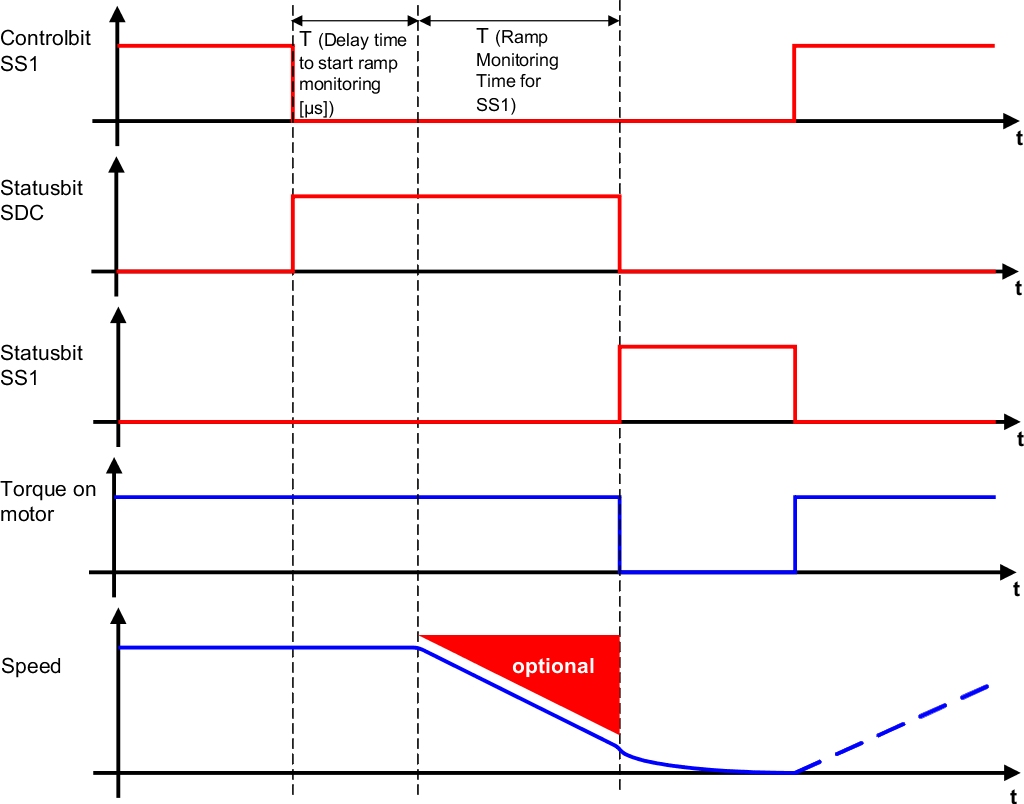
The Safe Stop 1 (SS1) safety function monitors a motor as it transitions from motion to standstill. When completely decelerated, safe pulse disabling is activated to cut off all torque and power to the drive. Depending on the requirements for the safety function, it is possible to monitor either only the deceleration time or the deceleration ramp. If the monitoring limits are violated during deceleration, safe pulse disabling is activated immediately and an error state requiring acknowledgment is triggered. One advantage of monitoring the deceleration ramp is that it reduces the assumed remaining distance to standstill when an error occurs.
SS2 - Safe Stop 2
SS2 - Safe Stop 2
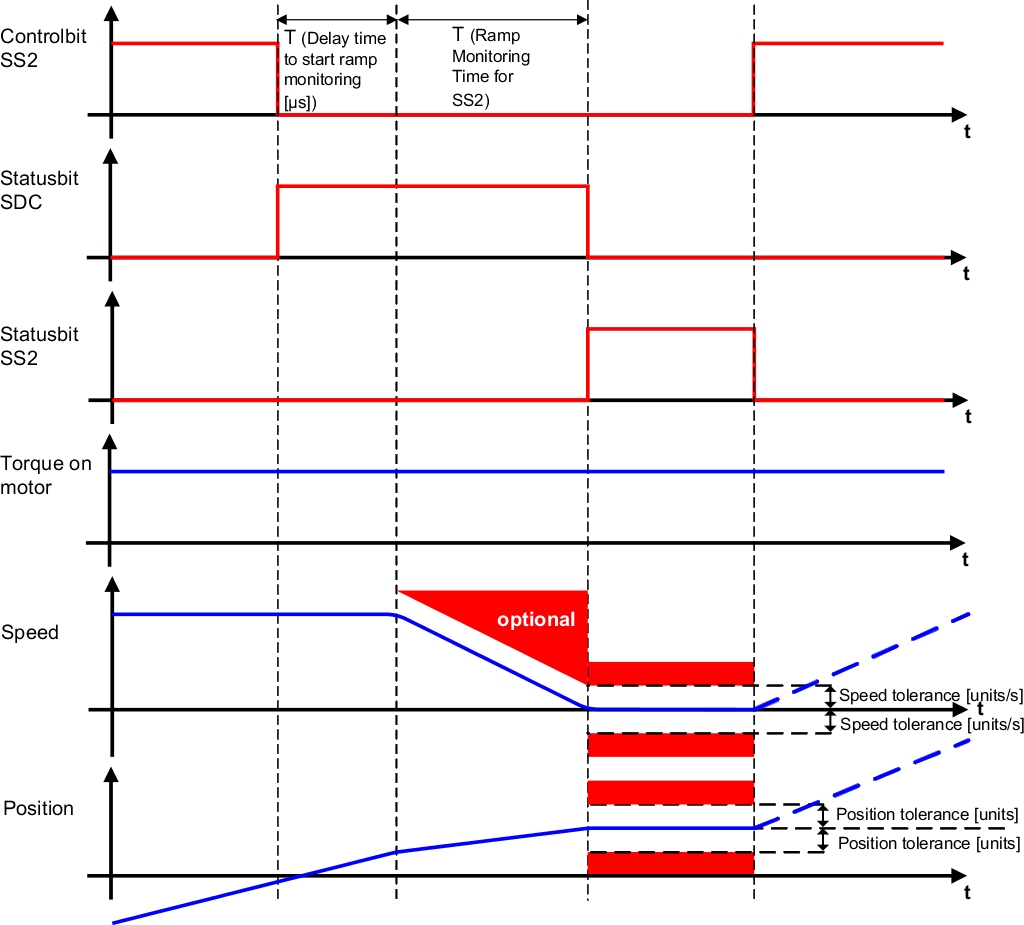
During Safe Stop 2 (SS2), transition of a moving motor to stop is monitored for safety. The drive must then be kept at standstill by the standard application. As with SOS, this standstill is monitored by the SafeMOTION module according to the configured standstill tolerance window.
As with SS1, it is possible to monitor either only the deceleration time or also the deceleration ramp depending on the requirements of the safety function. If a violation is detected during ramp monitoring or the subsequent standstill monitoring, safe pulse disabling is activated immediately and an error state requiring acknowledgment is triggered.
SLS - Safely Limited Speed
SLS - Safely Limited Speed

The SLS safety function monitors the drive to make sure that the configurable limits for speed are not exceeded. It is also possible to monitor deceleration until the limit is reached if needed by the application. Depending on requirements, deceleration ramp monitoring can be configured to either only monitor the deceleration period or to monitor the deceleration ramp as well. If a violation is detected during deceleration or when monitoring the limit speed, safe pulse disabling is activated immediately and an error state requiring acknowledgment is triggered.
SMS - Safe Maximum Speed
SMS - Safe Maximum Speed

The difference between SMS and SLS is that SMS cannot be actively requested. It is either enabled or disabled by the configuration. When enabled, the current speed is constantly monitored against a defined limit. If the limit is exceeded, safe pulse disabling is activated immediately and an acknowledgeable error state is triggered.
SDI - Safe Direction
SDI - Safe Direction
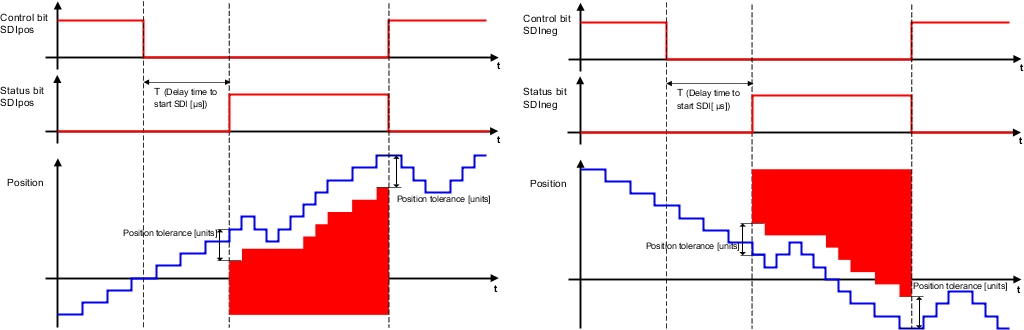
The SDI safety function monitors the defined direction of movement. If the interval is violated, safe pulse disabling is activated immediately and an acknowledgeable error state is triggered. Either the positive or negative direction can be monitored.
The safe direction function can be enabled in parallel with other safety functions.
For example, SLS can be limited to a certain direction.
SLI - Safely Limited Increment
SLI - Safely Limited Increment
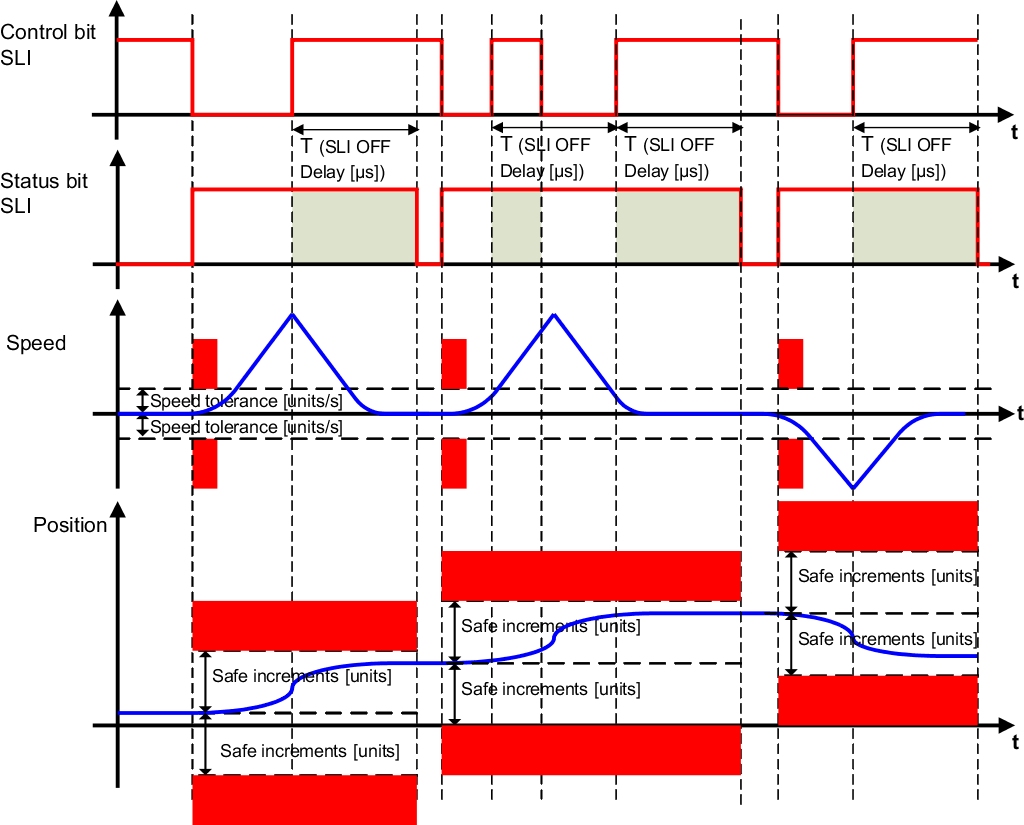
With the SLI safety function, a movement is monitored with respect to a defined number of increments.
The safe axis must be at a standstill when this function is enabled. A position window is then generated that is monitored from a safety point of view. This position window depends on the configured safe interval.
If the interval is violated, safe pulse disabling is activated immediately and an acknowledgeable error state is triggered.
SLA - Safely Limited Acceleration
SLA - Safely Limited Acceleration

The SLA safety function is used to monitor the acceleration or deceleration with respect to defined maximum limits.
The limits for acceleration and deceleration are monitored in the positive direction of movement.
The configured limits are monitored after the configured time has expired. This delay time compensates for the different runtimes of the standard and safety applications.
SBC - Safe Brake Control
SBC - Safe Brake Control
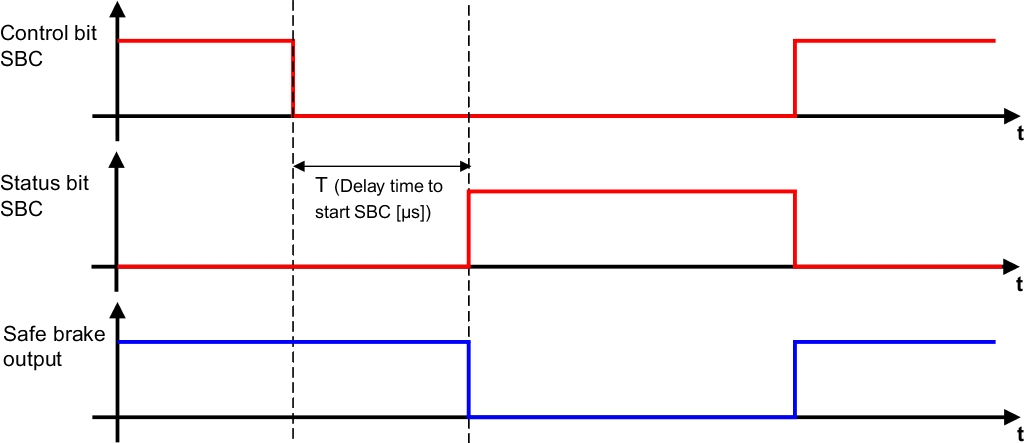
Safe Brake Control (SBC) sends a safe output signal to control an external brake. The SBC integrated safety function can be requested either explicitly via SafeLOGIC or when a module error occurs. Depending on the quality of the connected brake and its wiring, the function can fulfill SBC SIL 2 in accordance to EN 61508.
SLP - Safely Limited Position
SLP - Safely Limited Position
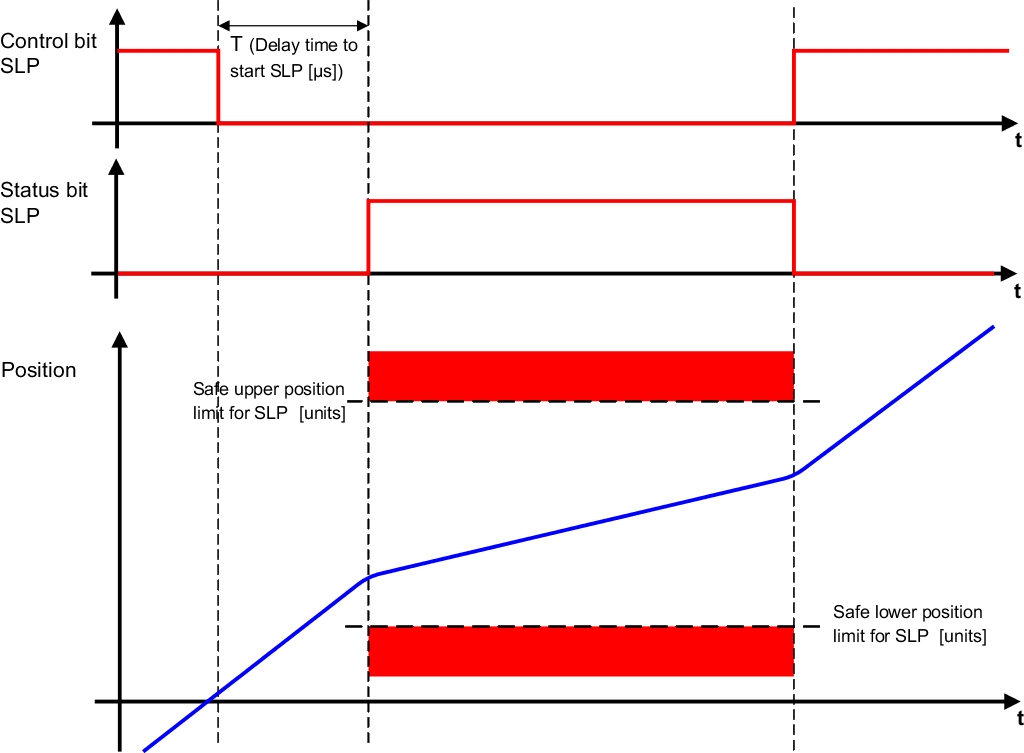
The purpose of the SLP safety function is to monitor a specified position window.
Parameters can be used to configure the lower and upper positioning limits of the monitoring range. When the position limit is approached, the monitored speed limit is calculated in such a way that the drive will come to a full stop before the positioning limit is reached using the configured deceleration ramp parameter.
SMP - Safe Maximum Position
SMP - Safe Maximum Position
The difference between SMP (Safe Maximum Position) and SLP is that SMP cannot be actively requested. It is either enabled or disabled by the configuration.
When enabled, the current position is constantly monitored against a defined position window. The SMP safety function only works with homed axes since it requires a safe absolute position.
As with the SLP safety function, the SMP function also monitors a position-dependent speed limit in addition to the position in order to minimize the remaining distance if the position window is exceeded.
Safe Homing
Safe Homing
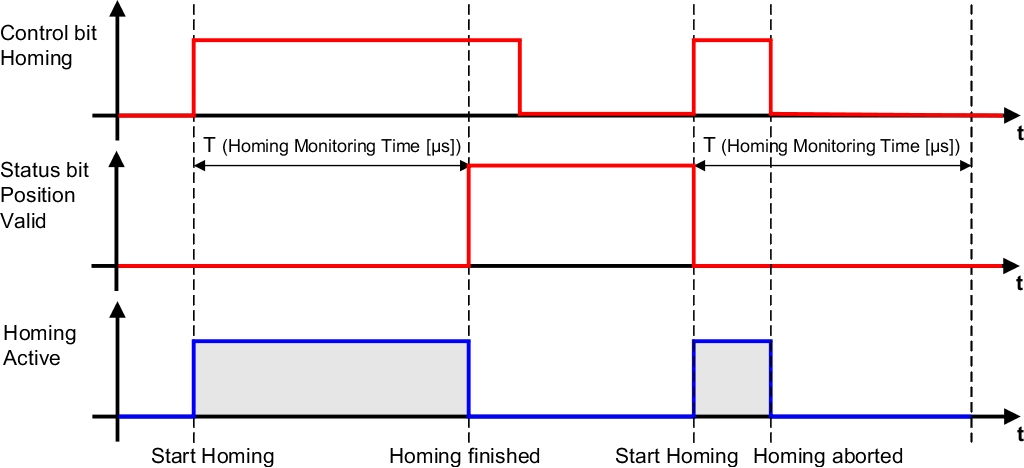
The Safe Homing function provides a way to establish a reference between the encoder position and the machine position.
Depending on the homing mode, it may be necessary for the drive to perform a homing procedure. A homing procedure requires the control functions between the electronic controller and the drive motor to be active. Other safety functions might have to be selected in order to prevent a hazardous state during the homing procedure.
SBT - Safe Brake Test
SBT - Safe Brake Test

The SBT (Safe Brake Test) safety function allows an engaged brake to be tested by applying a configurable stator current for a certain period of time.
The SBT safety function is not a conventional safety function! It is only used to test an engaged holding brake by applying a configurable stator current for a certain period of time.
The test is carried out at the specified safety level and with the specified precision.
RSP - Remanent Safe Position
RSP - Remanent Safe Position

With the RSP safety function, after the safe position has been homed once to the machine position, the homed safe position does not have to be homed again after a power off/on cycle.
It is only possible to store valid position data after a controlled standstill of the drive. The standstill must therefore be ensured. It must also be ensured that no power is supplied to the drive while the data is being saved so that it is not possible for the drive to move. These requirements are met when using the STO and SOS safety functions.